Tailored
Services
Creating Value
by making logistics part of business strategy
Logistics have become central to product strategy because, it is increasingly clear, products are not just things-with-features. They are things-with-features bundled with services. Companies do not create value for customers and sustainable advantages for themselves merely by offering varieties of tangible goods. Rather, they offer goods in distinct ways, presuming that consumers value convenience, reliability, and support. They are in an implicit and complex relationship with customers.
The challenge is to manage the whole of it. Pyramis Cargo offers Tailored Services that help businesses go beyond by making logistics a part of the business strategy. Value is created by allowing businesses to develop newer products and expand to newer markets, with logistics not being an impediment, but a value creator.

Our Tailored Services
Definition of Terms
Project Logistics
It is defined as the integrated planning, organisation, management, processing and control of the entire flow of materials and goods as well as the associated information flows. Starting with approach planning and the various stages of the purchasing value chain, logistics then covers production, followed by product delivery to the customer, as well as waste disposal and recycling.


Over Dimension Cargo (ODC)
In road transport, an over dimension cargo is a load that exceeds the standard or ordinary legal size and/or weight limits for a specified portion of road, highway or other transport infrastructure, such as air freight or water freight. There are also load per axle limits.
Break Bulk (Chartering)
It refers to cargo that needs to be individually loaded. Break bulk cargo cannot be shipped in inter-modal containers or in bulk, like grains or oil.


Exhibition Cargo
It is quite simply logistics service From your door to the event site. It includes freight forwarding, customs clearance, delivery to the event site and once the event is finished, recover materials and ship them back to your door or next show destination.
Carnet Services
A Carnet or ATA Carnet (pronounced kar-nay) is an international customs and temporary export-import document. It is used to clear customs in 85 countries and territories without paying duties and import taxes on merchandise that will be re-exported within 12 months*. Carnets are also known as Merchandise Passports or Passports for Goods.


Goods on Hanger
Garment on Hanger (GOH) (also known in certain circles as Hangtainer) containers are standard/dry containers that are converted/outfitted to be able to safely and conveniently carry garments on hangers – the same way you see them hanging in all the major retail stores..
Cross Trade
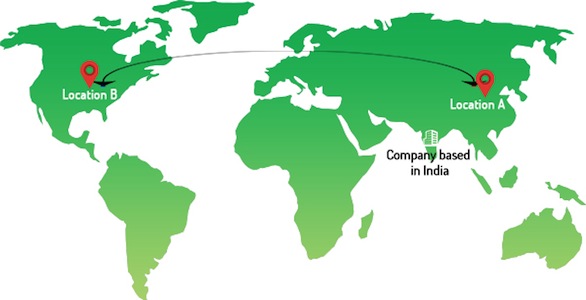
Cross Trade shipment is cargo that is freighted either by air and/or sea from one country to another country but not through your homebase where you are currently based. It involves issue of switch bill of lading. Example: An India-based company will send cargo from Location A to Location B without the goods being routed through India.
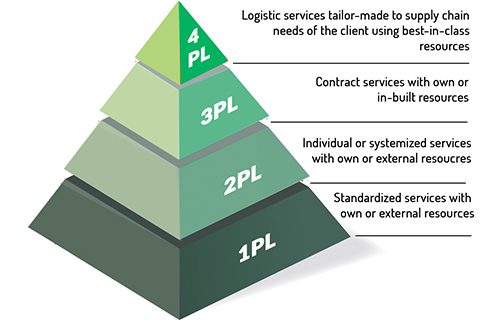
3PL Services
A 3PL (third-party logistics) is a provider of outsourced logistics services. Logistic services encompass anything that involves management of the way resources are moved to the areas where they are required. The term comes from the military.
4PL Services
The concept of a 4PL (fourth-party logistics) provider is an integrator that accumulates resources, capabilities and technologies to run complete supply chain solutions. Main Difference between 3PLs and 4PLs. The 3PL targets a single function, whereas the 4PL manages the entire process. A 4PL may manage the 3PL.
Hazardous Goods
They are materials or items with hazardous properties which, if not properly controlled, present a potential hazard to human health and safety, infrastructure and/ or their means of transport. The transportation of dangerous goods is controlled and governed by a variety of different regulatory regimes, operating at both the national and international levels. Prominent regulatory frameworks for the transportation of dangerous goods include the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, ICAO’s Technical Instructions, IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations and the IMO’s International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code.





